With Octopus Deploy the machines and services you deploy your software to are managed on the Infrastructure tab of the Octopus Web Portal:
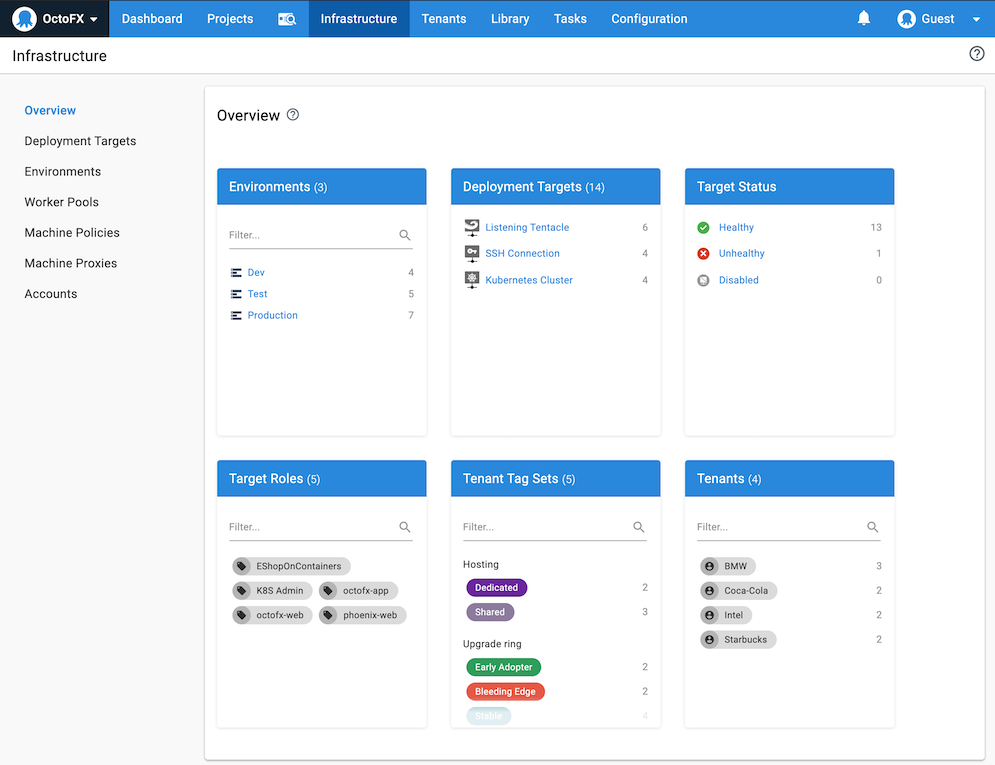
Deployment Targets
With Octopus Deploy, you can deploy software to Windows servers, Linux servers, Microsoft Azure, AWS, Kubernetes clusters, cloud regions, or an offline package drop. Regardless of where you’re deploying your software, these machines and services are known as your deployment targets.
Deployment targets are defined as the following. Octopus Deploy will count deployment targets differently against your license based on your license type.
- PTM License (Projects/Tenants/Machines) - Has at a project limit with optional tenant and machine limits in the license key. Sold from 2023 onward.
- Per Target License - Only has a target limit in the license key, no project or tenant limits appear in the license key. Sold between 2017 and 2024.
Please note: If you are unsure of your license type, please refer to your invoice or reach out to sales@octopus.com and they will clarify your license type.
| Host | Machine Count Against License (PTM) | Target Count Against License (Per-Target) | Important Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server running a Tentacle | 1 Machine per Tentacle instance | 1 Target per Tentacle instance | Listening Tentacles registered multiple times on the same instance will count as one (1) target. |
| Linux Server running a Tentacle | 1 Machine per Tentacle instance | 1 Target per Tentacle instance | Listening Tentacles registered multiple times on the same instance will count as one (1) target. |
| SSH Connection | 1 Machine per SSH Connection | 1 Target per SSH Connection | |
| Kubernetes agent | 0 Machines per Kubernetes Agent | 1 Target per Agent instance | |
| Kubernetes Cluster | 0 Machines per Kubernetes Cluster | 1 Target per Kubernetes Namespace | A namespace is required when registering the Kubernetes cluster with Octopus Deploy. By default, the namespace used in the registration is used in health checks and deployments. The namespace can be overwritten in the deployment process. |
| AWS ECS Cluster | 0 Machines per ECS Cluster | 1 Target per ECS Cluster | |
| Azure Web App / Function / Cloud Service | 0 Machines per Web App / Function | 1 Target per Web App / Function | This represents how Octopus Deploy currently counts Azure Web Apps / Functions. However, one (1) Azure Web App / Function is not equal to one (1) Linux server. |
| Azure Service Fabric Cluster | 0 Machines per Cluster | 1 Target per Cluster | |
| Offline Package Drops | 0 Machines per Offline Package Drop | 1 Target per Offline Package Drop | |
| Cloud Region | 0 Machines per Cloud Region | 0 Target per Cloud Region | Cloud regions are legacy targets that pre-dated workers as a mechanism to run scripts on cloud providers. They are used today to execute scripts multiple times with variables scoped for each iteration. |
Please note: Octopus will only count Windows Servers, Linux Servers, ECS Clusters, Kubernetes Clusters, etc., that are registered with an Octopus Deploy Instance. If you have 5,000 Linux Servers, and 4,000 of them are registered with Octopus Deploy, then Octopus will only count those 4,000 against your license.
You can manage your deployment targets by navigating to Infrastructure ➜ Deployment Targets in the Octopus Web Portal:
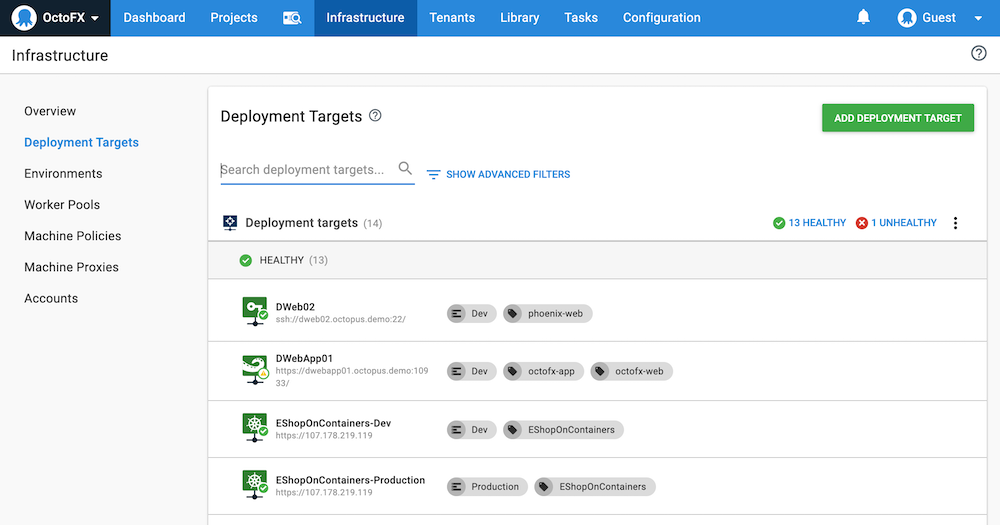
Learn more about deployment targets.
Environments
Before you can add your deployment targets to Octopus, you need to configure your environments. Environments represent the different stages of your deployment pipeline and ensure that the software that’s deployed is the same as it moves through those stages from, for instance, development, into test, and finally to production.
Typical environments include:
- Development
- Test
- Production
You can add as many or as few environments as you require in your deployment pipeline, and you can add as many deployment targets to each environment as you need.
Learn more about environments.
Workers
Workers are machines that are used to execute tasks that don’t need to be performed on the Octopus Server or specific deployment targets. Examples of such tasks include deploying a package to an API or running a script. You can register multiple workers and assign them to worker pools.
Learn more
Help us continuously improve
Please let us know if you have any feedback about this page.
Page updated on Wednesday, October 4, 2023
